From the outset, the subject of electric car charging cables can look befuddling. Such huge numbers of different fitting types, such huge numbers of different charging speeds! In any case, we’re here to assist you with making sense of what goes where, and which does what.
Before we hop in, it’s acceptable to realize that the force rating of chargers and charge points is given in kilowatts, or kW for short. Extensively, a higher number is better, however, we’ll get into that underneath.
The Cables
Whichever electric vehicle you purchase, you’ll likewise get a lot of charging cables. What you’re ensured to discover is a solitary arrangement of cables, with a residential 3-nail attachment to one end, and the right fitting sort for your vehicle on the other.
That is ideal for charging your vehicle at home, yet you’ll require an entire another link for connecting your vehicle to one of the numerous charge points you’ll discover when you’re all over the place. It’ll most likely be the situation that your vehicle does accompany the two arrangements of cables, yet if not, you can buy the correct link for charging in a hurry from the producer, or one of the numerous respectable online retailers.
Plugs and Connector Types
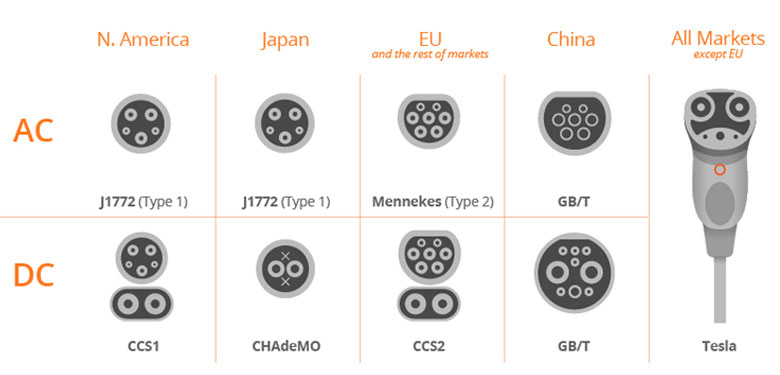
You may imagine that when somebody had the brilliant thought of presenting electric cars, they’d set an all-inclusive fitting sort and attachment for all cars to utilize. Lamentably, it’s more similar to the universe of cell phones, where different organizations utilize different connectors to charge their gadgets. The kind of connector you’ll require relies upon the charger type and its attachment, just as the attachment on the vehicle itself. Different chargers utilize different connectors, contingent upon the kW rating.
On the vehicle-side, there are two attachment types. European producers utilize a Type 2 gulf attachment with CCS rapid standard fitted, while Asian makers lean toward a Type 1 and CHAdeMO channel attachment. You’ll see that the link appended to a rapid charger has a beefier fitting contrasted with quick and moderate chargers – that is the piece of the attachment that uses the CCS which means the vehicle can get to rapid charging where accessible.
Combined Charging
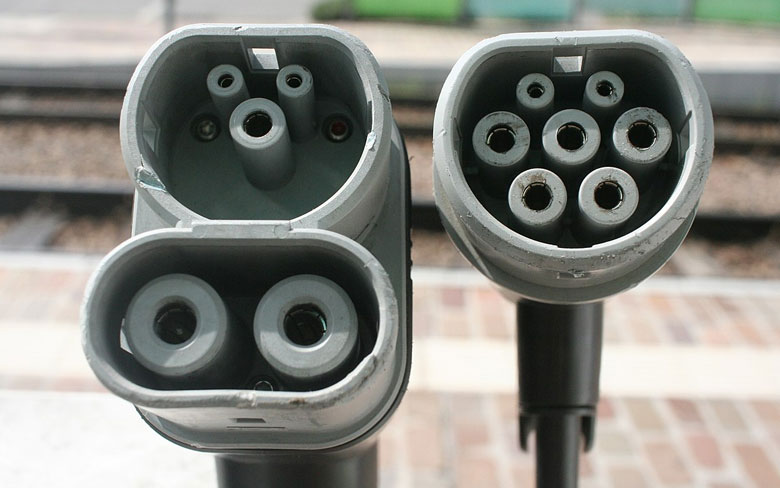

The Combined Charging System (CCS) is a combined charging system for charging electric vehicles with substituting flow (AC) and direct flow (DC). Both AC and DC Vehicle Connectors can be charged through the Vehicle Inlet, which implies that just a single interface is required in the vehicle. The Combined Charging System (CCS) is institutionalized in IEC 62196-3 and SAE J1772. Connector geometries are accessible for Type 1 (North America) and Type 2 (Europe). The system was created in a joint effort with driving car producers and is now utilized in an enormous number of electric vehicles. In 2013, the European Commission indicated the utilization of the CCS Type 2 charging system as per IEC 62196 as a uniform standard all through Europe.
Rapid Charging

Intended to be utilized to revive your car and unplugged when your car arrives at 80% of charge. It is acceptable behavior to remain with your car and move it when you are done. Move to another space or proceed on your excursion. Rapid Chargers have the link connected to the gadget and are found at Motorway Services and strip malls. There are at present two contending benchmarks. It is normally one that will get liked. You can buy rapid chargers from us we are EV Cable Supplier.
Different Charger Speeds
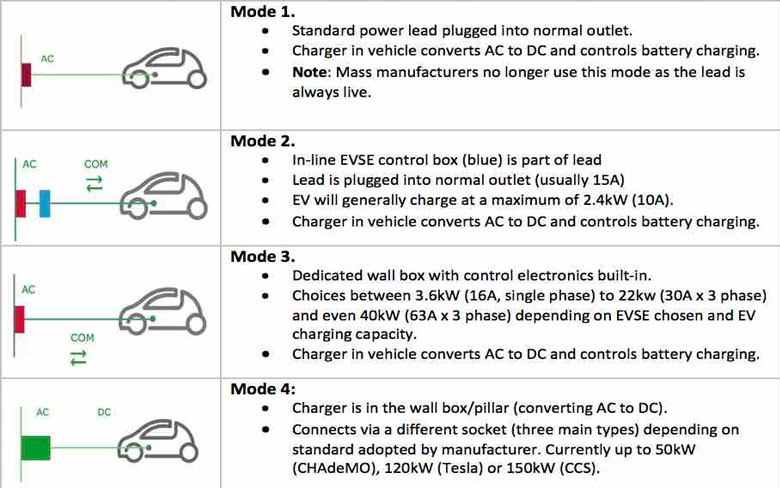
Charging speeds are part of three classifications – slow, quick, and rapid. Those classifications may appear to be genuinely plain as day, yet there’s more fine-grained detail you ought to know about. Slow chargers are appraised up to 3kW and incorporate charging at home from a 3-pin residential attachment. Since the kW rating on moderate charging is low, this implies the time it takes to charge a battery to 100% is longer. Truth be told, it can commonly take as long as 12 hours, so it’s ideal to utilize this charging speed in case you’re connecting medium-term.
Quick chargers are – you got it – somewhat quicker than moderate chargers. They’re appraised at either 7kW or 22kW, contingent upon the charging unit speed, and you’ll see them regularly in car-leaves or outside places of business. Bounce up to the universe of rapid charging, be that as it may, and you’ll encounter potential charging speeds of up to 120kW, accepting you have a good vehicle. Rapid chargers can energize a battery to 80% in as meager as 30 minutes – a genuine distinct advantage. They’re found at places like motorway administration stations.






